What Is Cloud Computing and Why It Matters
Cloud computing is more than a trendy buzzword in the tech world; it has become a necessity for businesses across industries. Offering everything from storage solutions to powerful computation capabilities, cloud services have revolutionized how businesses operate, scale, and compete in the digital age.
A way to look at cloud computing as a service is similar like electricity/power, food or water – we are very used to not producing our power or channeling our own water to our workplaces or households, same like we don’t produce the food we eat, but rather choose to buy ingredients and then prepare the final meal.
Infrastructure and computing related services have become both very complex maintain and essential for business at the same time. Therefore, IT is not something you want to do sporadically, fleetingly and leave to chance.
This guide explores cloud computing, its types, service models, and key benefits. By the end, you’ll understand why adopting cloud solutions is a game-changer for businesses of all sizes and from what your business might benefit.
A Brief History of Cloud Services
While the term “cloud computing” gained popularity in the 2000s, the idea has existed much longer. It can be traced back to the 1950s when mainframe computers enabled shared access to computing resources. The concept evolved significantly in the 1990s as the internet became widespread, laying the groundwork for modern cloud technology.
Today, tech giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform dominate the space, offering scalable and cost-efficient cloud solutions that empower businesses globally, but they are definitely not the only and often not the best option for every business
What Is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, software, and analytics over the internet, often referred to as the “cloud.” Instead of purchasing and maintaining physical IT infrastructure, companies can rent these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, providing a more flexible and cost-effective solution. This model eliminates the need for high upfront capital investments in hardware and reduces ongoing maintenance costs. Additionally, cloud computing offers the scalability to quickly adjust resources based on fluctuating business demands, whether it’s scaling up during peak usage or scaling down to save costs during quieter periods. This flexibility, combined with access to advanced tools and global infrastructure, makes cloud computing a vital technology for businesses of all sizes.

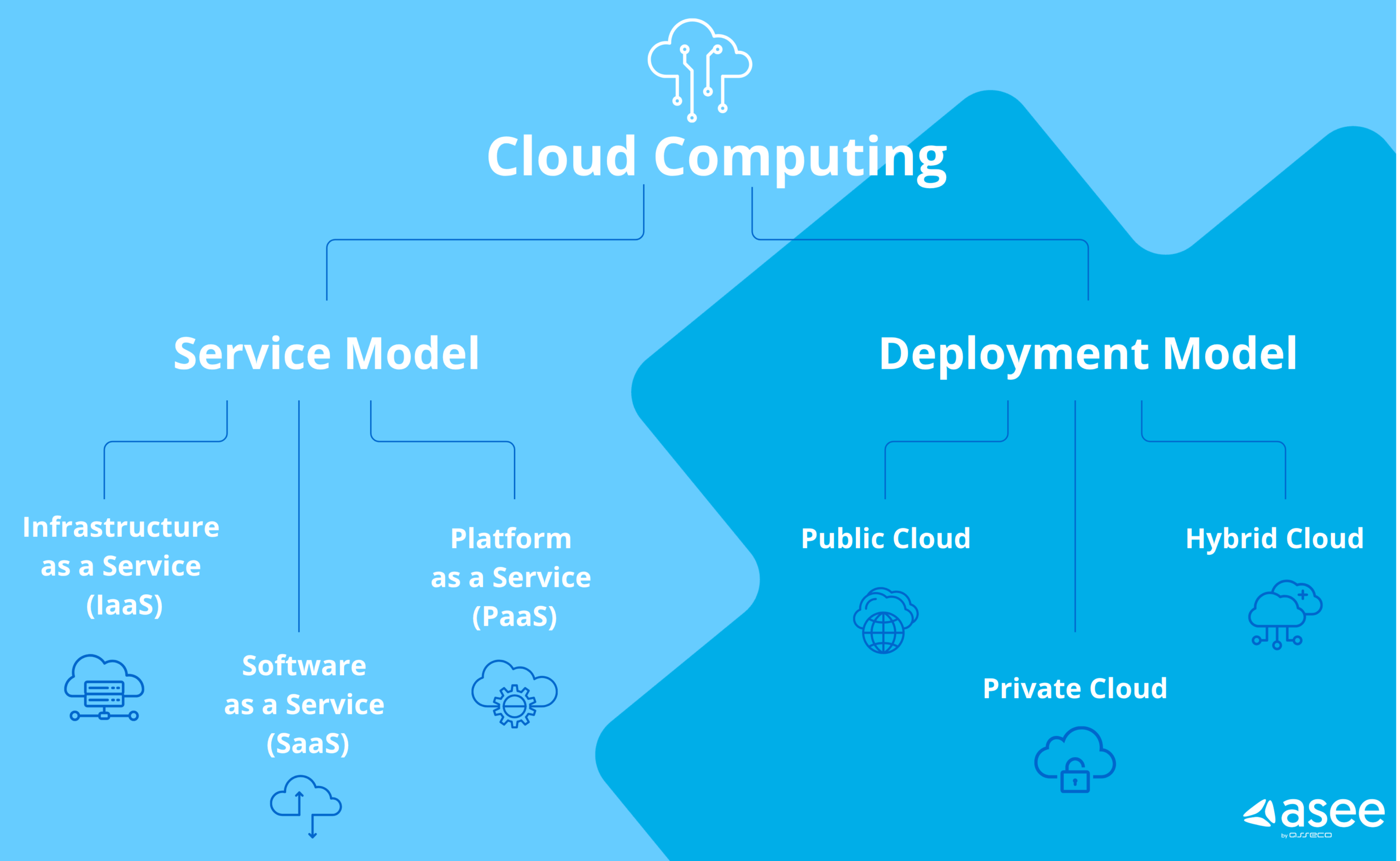
Types of Cloud Computing
Not all cloud solutions are created equal, which is why various deployment models exist. These models cater to different organizational needs and levels of control.
Public Cloud
A public cloud, like AWS (31% market share) or Microsoft Azure (21% market share), is owned and operated by third-party providers. Their infrastructures house shared resources such as servers and storage delivered to customers over the internet. Public clouds are scalable, cost-effective, and often best suited for small to medium-sized businesses.
Private Cloud
Private clouds are dedicated cloud environments for a single organization. Managed either internally or by a third party, private clouds are ideal for industries requiring stricter security and compliance, such as banking and healthcare.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud, which combines public and private clouds with on-premises infrastructure, sees rapid growth. By enabling data and applications to be shared between environments, it creates a flexible setup that offers an ideal balance of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and control.
Cloud Service Models
Cloud computing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Its service models address specific needs, from infrastructure to software solutions.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides basic computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking. Businesses can avoid the expenses and logistical challenges of physical hardware while maintaining control over operating systems and applications. Examples include AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers an environment to develop, test, and deploy applications without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure. This is particularly beneficial for software developers. Some popular PaaS solutions are Microsoft Azure App Services and Google App Engine.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Examples include Gmail, Dropbox, and Salesforce. SaaS eliminates the need for installations and manual updates, significantly reducing IT overhead.
Following our introduction that many companies are moving away from doing IT in-house, SaaS is the level on which business should start paying attention, have the chance to leverage on their strengths and provide an advantage to their end-clients.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has reshaped the business landscape by introducing a myriad of benefits that drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs.
- Cost Savings
Cloud solutions eliminate the need for upfront investments in hardware and reduce ongoing expenses related to maintenance and upgrades. The pay-as-you-go model ensures you only spend on the resources you use.
- Scalability
Cloud computing provides unmatched scalability, enabling businesses to adjust resources to match their needs. Whether scaling up for a new product launch or scaling down during off-seasons, the flexibility is invaluable.
- Enhanced Collaboration
With cloud-based tools, teams can collaborate in real-time, regardless of location. File-sharing platforms and project management software hosted on the cloud streamline communication and foster productivity.
- Global Reach
With data centers in geographically diverse locations, cloud providers enable businesses to reach a global audience while maintaining optimal performance and low latency.
- Improved Security
Contrary to misconceptions, cloud platforms offer robust security measures. These include data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regulatory compliance features that can mitigate risks.
- Disaster Recovery
The cloud offers reliable backup and recovery options by storing copies of data in multiple locations. This is invaluable for ensuring business continuity in case of unexpected events.
- Faster Innovation
With cloud platforms, companies can quickly deploy new features, services, or updates without being bogged down by infrastructural delays.

Why Cloud Computing Matters in Today’s Digital World
The importance of cloud computing goes far beyond cost savings or convenience. Industries like healthcare, finance, and retail are increasingly leveraging the cloud to gain competitive advantages.
- Banking Sector: Using private clouds for secure customer data storage and financial transactions. Responsibility for availability and compliance can be shifted to your cloud provider. For more insights, see our blog post on Why European Banks Should Consider EU Cloud Providers Over US Platforms.
- Retail Industry: Adopting public clouds to analyze customer behaviors and create personalized shopping experiences.
- Healthcare Providers: Implementing hybrid clouds to manage sensitive patient data while leveraging AI-driven insights.
Cloud computing also aligns with broader trends such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), which rely on expansive computational capacity.
Conclusion
Cloud computing isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift empowering businesses to thrive in an increasingly digital economy by focusing on what is their primary goal without having to worry about areas they do not excel in. Whether you’re a small startup eyeing scalability or a large enterprise needing robust security, there’s a cloud solution tailored to your needs.
Curious to see how cloud computing can transform your business?

Luka Mićanović
Share
More from ASEE
How Technology is Elevating Public Service Standards
Public institutions across Southeast Europe are facing growing pressure
How to Protect Your Mobile Device from Security Threats: 10 Essential Security Tips
Mobile devices are among the objects we use the most
Why Information Security Is Everyone’s Responsibility
New year, the same shared responsibility for information security.









